Understand Common Heart Problems and How Aging Can Influence Heart Health

Heart disease is a significant health concern for adults over the age of 40. It is the leading cause of death in the United States, affecting millions yearly.
As we age, our risk of developing heart disease increases. This is due to various factors, including changes in our bodies that occur with age, such as increased cholesterol levels and decreased physical activity.
Heart problems can lead to a higher risk of long-term health care in a variety of ways. Heart disease can cause damage to the heart muscle, leading to decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to other organs in the body. This can cause organ damage, leading to chronic health conditions such as kidney failure, stroke, and heart failure. Additionally, heart disease can increase the risk of developing other chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Additionally, aging and needing long-term health care itself can increase the chance of heart disease in older adults. Long-term health care often involves in-home care, living in an assisted living facility or nursing home, leading to a sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition. This can increase the risk of developing heart disease due to a lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating habits.
Variety of Heart Problems Can Develop with Aging
Many different types of heart problems can affect adults over 40, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, arrhythmias, and valvular heart disease.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart problem in adults over 40. It occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. This buildup can cause blockages that reduce or stop blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and even a heart attack.
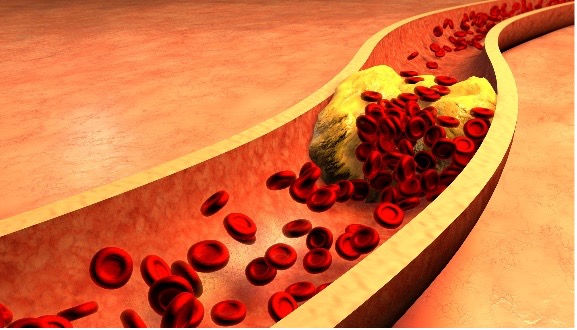
Risk factors for CAD include high cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Treatment for CAD includes lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and exercising regularly, as well as medications such as statins and ACE inhibitors.
Someone with CAD may need surgery to put in a stent. A stent is a small tube-like device that is inserted into a blocked artery to help keep it open. It is typically used in cases of coronary artery disease, where the arteries become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque.
A stent procedure may be recommended if lifestyle changes and medications are not enough to improve symptoms or if there is a risk of a heart attack. The procedure usually takes place in an operating room under general anesthesia and involves inserting a catheter into an artery in the groin or arm and guiding it up to the blocked artery. The stent is then expanded to open up the artery and restore blood flow.
Other common heart surgeries include coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve repair or replacement, and atrial septal defect (ASD) closure. CABG is a procedure in which a healthy artery or vein from another part of the body is used to bypass a blocked or narrowed coronary artery. This helps restore blood flow to the heart muscle.
While stents offer a minimally invasive way to reopen a blocked artery, bypass surgery also remains a leading treatment for people with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), says Tyrone Krause, MD, Chief of Cardiothoracic Surgery at Jersey City Medical Center.

We're all born with three major arteries to the heart. We use bypass surgery to give you one, two or three new pipes depending on the number of arteries blocked.
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is another common type of heart problem in adults over 40. CHF occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs and other organs, which can cause shortness of breath and fatigue.
Risk factors for CHF include high blood pressure, diabetes, coronary artery disease, obesity, and certain medications or toxins such as alcohol or cocaine use.
Treatment for CHF includes lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and exercising regularly, as well as medications such as diuretics and ACE inhibitors.
Arrhythmias are abnormal rhythms of the heartbeat that can occur in adults over 40 due to various causes, including coronary artery disease or other structural problems with the heart muscle itself. Symptoms may include palpitations (a feeling like your heart is racing), dizziness, or fainting spells due to low blood pressure caused by an irregular heartbeat.
Treatment for arrhythmias may include lifestyle changes such as avoiding caffeine or alcohol or medications such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, depending on the type of arrhythmia present.
Valvular heart disease occurs when one or more valves in your heart do not open properly, which can lead to a decrease in blood flow through your body's organs resulting in symptoms such as fatigue or shortness of breath with exertion.
Risk factors for valvular heart disease include age (over 65), family history of valve problems, rheumatic fever during childhood, certain infections such as endocarditis (infection of the inner lining of your heart), certain autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, radiation therapy to your chest area during cancer treatment, certain medications including some antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs used to treat cancer patients; treatment may involve lifestyle changes such as avoiding strenuous activity if you have severe valve problems or surgery if necessary depending on how severe your valve problem is.
Valve repair or replacement involves replacing a damaged valve with an artificial one or repairing the existing valve so it can function properly.
Gut Health and Heart Failure
New research is showing a connection between gut health and the risk of developing different diseases, including heart failure.
Stanley Hazen, MD, Ph.D., a specialist in cardiovascular medicine for Cleveland Clinic, says new research might be used to eventually develop drugs as a new treatment for heart disease.

We had previously shown that the gut microbiome produces a compound, we call it PAG. That contributes to heart failure, but we didn't know what the microbial sources for it were.
Dr. Hazen says that a healthy diet is just as important in terms of the prevention of heart disease.
The concept of having more vegetables in one's diet and eating less red meat or animal source products seems to be a recurring theme. Even though we aren't searching for that in our research, it keeps popping up, when we're really looking for what are the compounds in blood that track with the future development of disease.
Be Aware of Risk Factors
Being aware of their risk factors for developing any type of cardiovascular condition so anyone over age 40 can take steps towards prevention by making healthy lifestyle choices, including:
-
eating a balanced diet low in saturated fat and sodium
-
exercising regularly
-
quitting smoking
-
controlling weight
-
managing stress levels
-
getting regular checkups with your doctor
-
monitoring cholesterol levels
-
controlling blood pressure
-
managing any existing medical conditions
-
avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
-
taking prescribed medications correctly
-
getting vaccinated against flu viruses every year
Plus, being aware of any family history you may have regarding cardiovascular conditions is vital so you can take steps toward early detection if necessary.
Planning is always important, and taking proactive steps for your health, retirement plans, and long-term health care will reduce stress and help with a better quality of life.
Don't wait until you have health problems, including significant health issues, until you start thinking about your health and future long-term care planning.
Heart Problems and Long-Term Care Insurance
If you have an existing heart health issue, you may still be able to obtain Long-Term Care Insurance depending on the problem and how well it is being managed. A combination of heart problems and other health history, like diabetes, can make it harder to get coverage.
Seek the help of a qualified Long-Term Care Insurance specialist to help match your health, age, family history, and other factors to the right insurance company. A specialist who represents top companies is beneficial since every insurance company has its own underwriting standards.
Most people get coverage when they are in their 40s or 50s and still have reasonably good health.


